global positioning system (satellite comm.) (GPS)
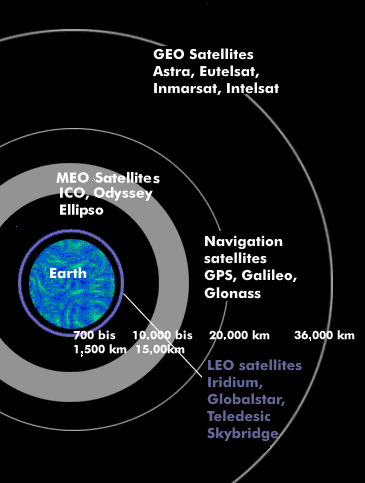
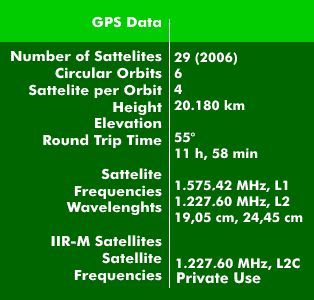
The GPS system is a worldwide US satellite navigation system for highly accurate positioning, navigation and time determination. The Global Positioning System (GPS), the actual name is NAVSTAR, has operated since its inception with 24 orbiting satellites (21 operational and 3 spare) in six different orbits at an altitude of 20,180 km. The orbital speed is 3.9 km/s or 11 hour and 58 minutes for one orbit around the Earth. There are now 29 active GPS satellites. The orbits are positioned above the MEO satellites in such a way that four satellites can be received simultaneously at all points on the Earth's surface
The GPS satellites are equipped with several caesium standards or rubidium standards, which generate a constant time with a long-term constancy of '10^-13'. From the fundamental frequency of the atomic frequency standards of 10.23 MHz, all required frequencies are derived. In addition to the high-precision time signals, each satellite transmits a typical recognition code and its orbital data.
Transmission techniques of GPS
The two transmitters of the GPS satellites use spread-band technology and transmit at the GPS frequencies of 1.57542 GHz and 1.2276 GHz. The transmitting power of the GPS satellites is only 50 W, which is causally responsible for the low data rate of 50 bps. The GPS signals are modulated in phase modulation.
GPS position determination can be carried out with two GPS satellites when locating at sea level. However, if altitude is also considered in the positioning, the GPS frames from at least three GPS satellites are required.
The positioning accuracy of GPS
The position accuracy depends on the switched service from and the deviation error, which is caused by the satellite positions and the interferences from the ionosphere. The degradation of accuracy is called Dilution of Precision( DOP). There are two resolution services: the Precision Positioning Service( PPS) for authorized institutions, primarily U.S. military, and the Standard Positioning Service( SPS) for civilian use. Accuracy is about +/-15 m for civil use after the repeal of Selective Availability( SA) in 2000; previously it was about 100 m; for military applications using the Precision Encrypted Code (P/Y code), it is below one meter. For private use, the height accuracy is 20 m and the time accuracy is about 60 ns.
Methods to improve the positioning accuracy
There are several methods that can be used to increase the accuracy of the GPS system for civil use. These systems, called SBAS systems, for Satellite Based Augmentation System (SBAS), and which use correction signals, include Wide Area Augmentation System( WAAS), European Geostationary Overlay Service( EGNOS), and Multi-Functional Satellite Augmentation System ( MSAS). There is also Differential Global Positioning System( DGPS), a technique that uses differential measurements of travel times to increase local resolving power to within a few meters.
The strategic competitor system initiated by the European Union is Galileo, the system developed by the former USSR is called Global Navigation Satellite System( GLONASS) and the Chinese system BeiDou.