global navigation satellite system (GNSS)
Global Navigation Satellite Systems(GNSS) are used for worldwide positioning, coordinate and time transmission. They are used in commercial areas in aviation and shipping, but also in automobile and rail transport. GNSS systems are used by the police, border guards, customs and the military, as well as by search and rescue services, and last but not least by logistics companies, aerial photography companies and private individuals.
Worldwide, there is the U.S. Global Positioning System( GPS), which was primarily designed for military tasks and is also used for civilian purposes with a reduced resolution. In addition, the Galileo satellite navigation system initiated by the European Union is being installed, which has broader applications than the GPS system. There is also the Russian Glonass navigation system and the Chinese Compass.
Satellite-based navigation systems
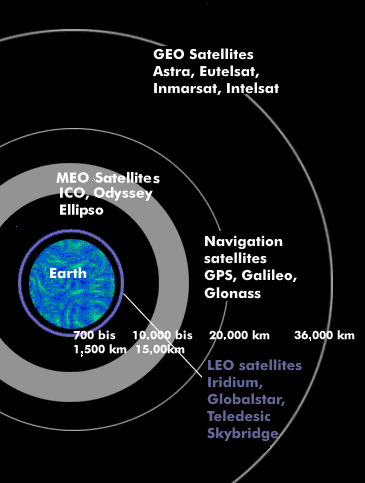
All satellite-based navigation systems operate near-earth satellites so that the mobile receiving devices can still receive the satellite signals. To determine position, the receiving device must be able to receive signals from at least three satellites simultaneously at any location on Earth, and preferably from four. In order to fulfill these basic conditions - proximity to the earth and simultaneous reception of three (four) satellites - satellite navigation systems must consist of at least 24 satellites, better 32. This ensures that a new satellite can always be received by the navigation device before another one enters the earth's shadow. Satellite navigation systems use MEO satelliteswith flight altitudes between 19,000 and 24,000 km that orbit the earth in geosynchronous trajectories. Glonass has a flight altitude of 19,100 km, GPS satellites orbit at 20,180 km, Compass satellites at 22,000 km, and Galileo satellites at 23,600 km. Various GNSS systems operate with backup satellites and GEO satellites through which communications are handled. All navigation satellites continuously transmit two signals: a high-precision time signal and a coordinate signal that indicates the current satellite position at a given time.
The position accuracy of navigation systems
Since the position accuracy of the GPS system for private use is limited compared to the highest possible position resolution, various methods have been developed with stationary and satellite-based systems that increase the position accuracy down to the centimeter range. These systems are called Satellite Based Augmentation Systems( SBAS). They include Differential Global Positioning System( DGPS), Differential Global Navigation Satellite System( DGNSS), European Geostationary Overlay Service( EGNOS), Wide Area Augmentation System( WAAS) and Precise Point Positioning( PPP).
The receiving side of satellite navigation is formed by navigation devices. These are purely receiving devices that receive signals from at least three satellites and calculate their own position on the earth from the time information, the satellite coordinates and the transit time.
In addition to the aforementioned methods for increasing position accuracy, there is also the multi-GNSS. This method works with a dual navigation device that can receive two navigation satellites simultaneously - GPS and Glonass - and combines both position values.