gallium arsenide (GaAs)
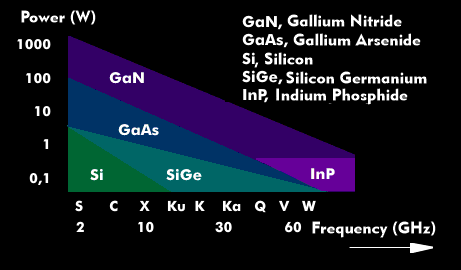
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is an amorphous compound semiconductor belonging to the group of III-V compound sem iconductors. Gallium arsenide has a band gap of 1.4 electron volts( eV) and is used in a wide variety of ultrahigh- frequency semiconductor devices, thin-film solar cells, and infrared LEDs.
Because gallium arsenide is characterized by extremely fast switching and low power consumption, it is found in the heterojunction bipolar transistors(HBTs) of ultrafast circuits for optical transmission, as well as in high electron mobility transistors(HEMTs) used to amplify microwaves, in low- noise amplifiers(LNAs), as RF power amplifiers in base stations, and in tiny monolithic microwave integrated circuits(MMICs). Gallium arsenide, however, cannot handle as high voltages as gallium nitride( GaN).
Furthermore, monocrystalline gallium arsenide is used in photovoltaics in thin-film solar cells and is characterized by an efficiency of 25%. Another field of application for gallium arsenide are devices for the emission of infrared light, for example semiconductor lasers, in which the substrate is made of gallium.