dynamic host configuration protocol (IP) (DHCP)
The DHCP protocol is a client- server protocol that reduces the effort required to assign IP addresses and other parameters. Using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), a network administrator can centrally manage and maintain all TCP/IP configuration parameters.
The DHCP protocol is used for dynamic and automatic end device configuration, e.g. the assignment of IP addresses under IPv4 and IPv6. The corresponding IP addresses are requested from the DHCP server by the connected DHCP clients. The addresses are taken from an address pool that resides in a DHCP server.
The IP address can be assigned automatically, dynamically or manually. With automatic assignment, the client is given a free address the first time it logs on to the network. With this type of address assignment, each address can only be assigned once and cannot be used for other clients. This is different with dynamic assignment. With this type of assignment, the address is assigned temporarily for a certain period of time. If the address is no longer needed by the client, the server can dispose of it again and assign it to another client. Manual address assignment allows the network administrator to assign an address to a client.
Because the DHCP protocol uses several Bootstrap Protocol( BootP) commands and supports BootP relay agents defined in the Bootstrap protocol, the DHCP protocol can be viewed as an extension of the older, static Bootstrap protocol that is being replaced by DHCP. DHCP is considered more secure and easier to manage.
Message types of the DHCP protocol
The DHCP protocol knows several message types, which are used to control the entire information exchange between client and server. The client's request is made by a broadcast (DHCP Discover) to test the network for different DHCP servers. In response, the DHCP server sends a broadcast or unicast message(DHCP Offer) in which a configuration is submitted to the client. If the DHCP client accepts the offered configuration parameters, it sends a DHCP request via broadcast. The server then uses DHCP ACK to send the configuration parameters and the IP address. If a DHCP server rejects a request regarding certain configuration parameters, it sends a NAK signal to the client. If the network address is no longer required by the client, it sends a DHCP release to the server.
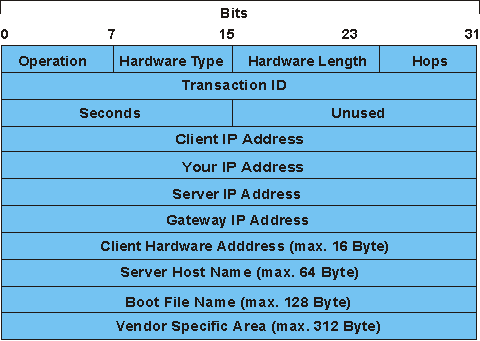
Certain messages must be sent as a broadcast on both the server and client sides so that all other clients and servers are informed about the configuration and do not reserve addresses and configurations unnecessarily. The structure of the DHCP frame format is identical to that of the BootP data frame except for the flag field and the option field, which are not used or are used differently in BootP. The DHCP protocol is described in RFCs 1541, 1542 and 2131.