damping factor (DF)
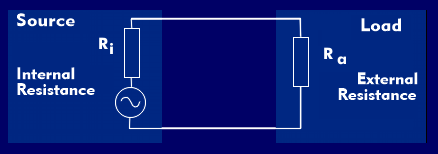
The damping factor (DF) is a characteristic value of audio components. It is dimensionless and defined as the quotient between the load resistance(Ra) and the internal resistance( Ri) of the audio component (Ri) at a frequency of 1 kHz (DF = Ra/Ri).
Amplifiers and power amplifiers have attenuation factors of 100 and higher. The internal resistance of an amplifier is the quotient of the load resistance and the attenuation factor: Ri = Ra/DF.
The damping factor determines, among other things, the settling and decay of amplifiers when signals are applied to them. The more abruptly the signal ends and the shorter the decay time, the higher the damping factor. The effects of a low or high damping factor can be heard when a loud sound ends abruptly. With a low damping factor, the decay of the sound takes a certain amount of time, which is reduced with a higher damping factor. On the other hand, too high an attenuation factor has the negative effect of clipping high signal peaks and reproducing them as dry, dull sounds.
In loudspeakers, the damping factor is affected by self- induction. Every time the diaphragm moves, a voltage is induced in the speaker coil that counteracts the diaphragm excursion and loads the output of the power amplifier.