crossover
Inacoustics, crossovers are passive or active crossovers used to split the frequency of the loudspeaker signal for the various speakers in a loudspeaker cabinet.
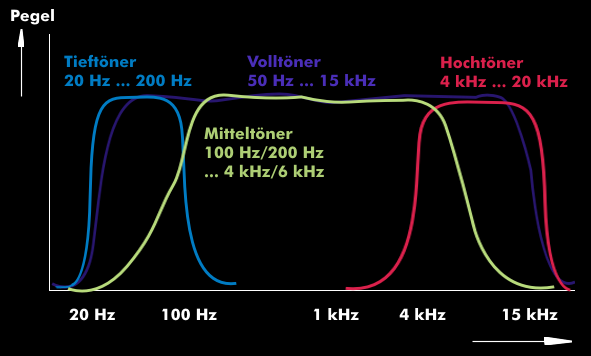
The audio frequency range is between 20 Hz and 20 kHz, which corresponds to a wavelength range between 17 m for a 20 Hz oscillation and 1.7 cm for a 20 kHz oscillation. Such an extensive wavelength range can only be covered with multiple loudspeakers. For this reason, the entire audio frequency range for tweeters, midrangedrivers, woofers and subwoofers must be frequency-divided for the drivers via high-pass filters, band-pass filters and low-pass filters. Conceptually, the crossovers can prepare the frequency ranges for two, three or even more drivers. Since the individual frequency ranges overlap somewhat (crossover), the term crossover is used for this.
The filters used in the crossovers characterize with their slope the separation between the frequency ranges of the individual loudspeakers. Typically, the slopes are 6 dB/ octave or 20 dB/ decade or 12 dB/octave, but they can be increased up to 24 dB/octave with higher orderfilters. During crossover, the filter edges overlap.
In addition to frequency separation, crossovers also stabilize impedance loading from the speakers. In addition, some offer the ability to adjust the volume level to optimize the sound image.
Passive crossovers consist of coils, capacitors and resistors and are load dependent. Active ones are based on integrated circuits( IC) and discrete transistors. They are load-independent and provide impedance buffering.