advanced microcontroller bus architecture (AMBA)
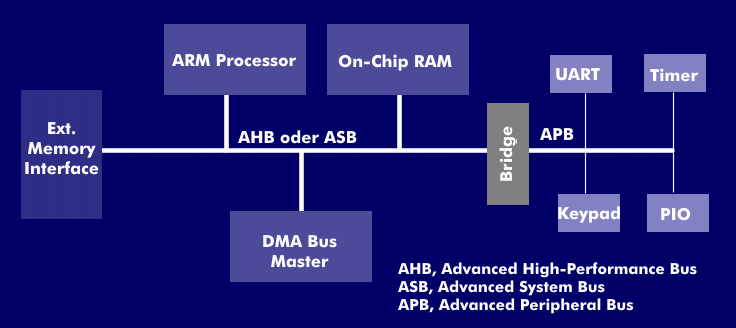
System-on-chips(SOC) have special requirements for the bus systems via which individual functional units communicate with each other. Advanced RISC Machines Limited( ARM) developed the Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture (AMBA) for these applications.
In the meantime, the AMBA architecture is not only used in SoC-based microcontrollers, but also in ASICs (Application Specific Integrated Circuit) and SoC application processors such as those used in smartphones. The first buses of the AMBA architecture were the Advanced System Bus( ASB) for high- performance system components and the Advanced Peripheral Bus( APB) for peripheral components with low power consumption. Later, the AMBA High-Performance Bus( AHB) was added, and in the third version, the Advanced Trace Bus( ATB), which has even higher performance.
The AMBA architecture with its various bus systems forms a de facto standard for embedded 32-bit processors. The system supports system buses with bus widths of 32, 64 and 128 bits. These are synchronously operating, non-multiplexed buses that support bursting and pipelining.