acoustics short circuit
An acoustic short circuit is an acoustic phenomenon in which sound waves radiated from loudspeakers cancel each other out.
This phenomenon occurs when the sound wave radiated from the front of a diaphragm can reach the back of the diaphragm unimpeded. As a result, pressure equalization takes place because loudspeakers compress the pressure on the front side of the loudspeaker and cause a reduction in pressure on the back side of the loudspeaker. This means that the pressure conditions in front of and behind the loudspeaker act in opposite directions and compensate for each other.
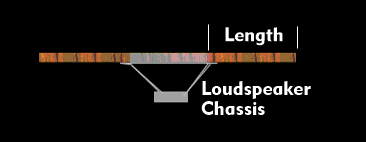
Only when the air path between the front and rear of the loudspeaker is lengthened, and the time this takes, can the acoustic vibrations no longer be eliminated. This pressure equalization is prevented by baffles and loudspeaker chassis. In this case, the radiated sound wave cannot travel directly to the back of the diaphragm, but the sound path is extended. To prevent an acoustic short circuit, the path of the sound wave must be longer than its wavelength. The path is extended via the baffle, loudspeaker box, transmission line box or bass reflex box.