accumulator
The term accumulator occurs in memory technology and is also used for rechargeable batteries, the secondary cells.
The accumulator as memory register
The accumulator is the memory register of the arithmetic unit, which is connected to the main memory via the data bus. Since the arithmetic unit( ALU) requires two operands for all mathematical operations, one operand is loaded from the main memory via the data bus into the accumulator, where it is temporarily stored for the operation. The result of the calculation performed by the arithmetic unit is then stored again in the accumulator and stored in the working memory via the data bus.The accumulator as a rechargeable energy source
An accumulator is a rechargeable DC energy source in which the electrical energy is obtained from an electrochemical reaction. Unlike a battery, which is called a primary cell, an accumulator is a secondary cell. In English, the rechargeable battery is called a rechargeable battery. Current output and current consumption are based on electrochemical reactions.Structure of rechargeable batteries
A rechargeable battery consists of two electrodes, the cathode and the anode, which are located in an electrolyte, a solid substance or a liquid. The electrolyte provides transport for the ions produced by the chemical reaction with the electrodes. The chemical reaction and the associated charge transfer within the battery are always associated with a current flow outside the battery. The charge is balanced by means of cations and anions via the electrolyte. The anode converts the anions into electrons and conducts the flow of electrons through to the electronic circuit. In addition to standard rechargeable batteries with liquid electrolyte, there are solid batteries whose electrolyte is solid.Characteristics of rechargeable
batteries Performance parameters of rechargeable batteries are the electromotive force ( EMF), the nominal capacity in ampere-hours( Ah), the energy density in watt-hours per weight(Wh/kg), the power density in W/kg, the internal resistance in milli-ohms, the self-discharge, the discharge current and C coefficient, the number of charge cycles and the related memory effect, the state of charge, State of Charge( SoC), the state of discharge, Depth of Discharge( DoD) and the battery state, State of Health ( SoH). There are also intelligent batteries, Smart Batteries, which indicate the state of certain characteristic values. The nominal voltage of rechargeable battery cells depends on the materials used and thus on the electrochemical voltage series and can range from +2.9 V to -3.0 V. In commercially available rechargeable batteries, the source voltage for a battery cell is 1.2 V, in contrast to batteries, whose nominal voltage is 1.5 V.Designation systems for rechargeable batteries
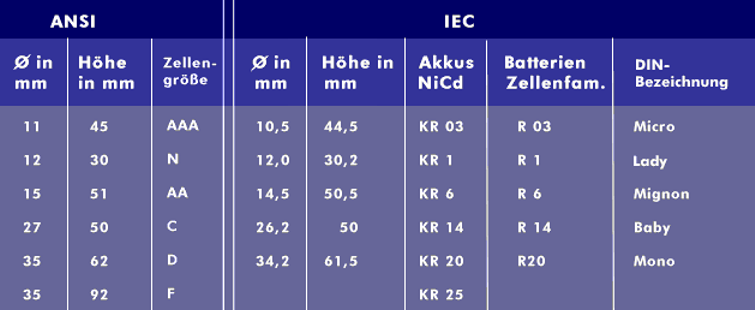
rechargeable batteries The size of rechargeable batteries is defined by ANSI, the International Electrotechnical Commission( IEC) and DIN. In addition to these designations, there is a designation system for round cells introduced by Japanese companies, which is formed from the diameter and the size. For example, there is the size 18650, which states that the battery has a diameter of 18 mm and an overall height of 65 mm. The best-known batteries used in mobile communications and portable devices are the NiCd battery, NiMH battery and various lithium batteries of which the lithium-ion battery and the lithium-polymer battery are currently the best known because of their compact design. A cheaper alternative to the LiIon battery is the sodium-ion battery, and the lithium-sulfur battery is currently being developed as a powerful replacement with an extremely high energy density. The classic lead-acid battery is generally known from automotive technology.