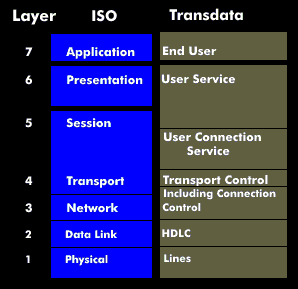
Transdata
Transdata is a hierarchy-free network architecture from Siemens that was developed as a proprietary architecture for communication in distributed systems in the 1970s. It is equally a universal communication concept and a network architecture. The communication concept represents objectives and blueprints for solving communication tasks, while the network architecture forms the set of rules for protocols and interfaces.
The development of Transdata took place in several stages. It started with networks with programmable DÜ control, followed in stages 2 and 3 by the use of data transmission precomputersand network nodes. In stage 4 the Transdata architecture was extended and with the Data Communication Method( DCM) came a new communication concept, which in the following stage was extended by data station computers and for the first time provided a connection to the System Network Architcture( SNA). In the 1980s, the 6th stage added distributed data processing, central network management and local data stations. This was followed by interfaces for the public networks of the time, such as Datax-P, Datex-L and Btx, and in the mid-1980s, distributed network management and the opening towards Open System Interconnection( OSI) were added.
The data stations, station computers, network nodes and data transmission precomputers involved in Transdata operate with Data Communication Method (DCM) as the access system in the processing computer and with High Level Data Link Control( HDLC) as the transmission protocol.