RAID 4
RAID level 4, also called " block striping with parity disk", works with completely separate drives and separate storage of the parity data on respectively assigned drives.
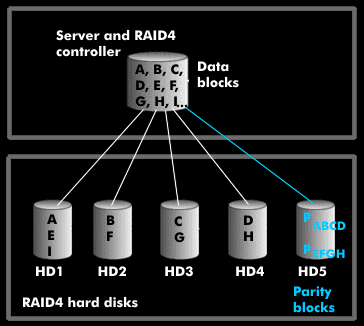
RAID 4 is similar to RAID 3, but the data is distributed to the user disks in blocks and the parity is stored on a shared parity disk.
Assuming RAID 4 works with five drives, the data blocks (A, B, C, D, E,...) are written to the four disks 1 (A), 2 (B), 3 (C) and 4 (D) one after the other. The following data blocks are again written consecutively to the four drives, and so on. This distribution of data blocks is called striping.
The fifth disk is the parity disk. The parity blocks are written to it as an XOR operation: P(ABCD) = A XOR B XOR C XOR D. If one of the hard disks fails, one can reconstruct the missing or faulty data block from the parity blocks and the data blocks from the other drives. On the other hand, every change in a data block results in a recalculation of the parity block.