NGN architecture
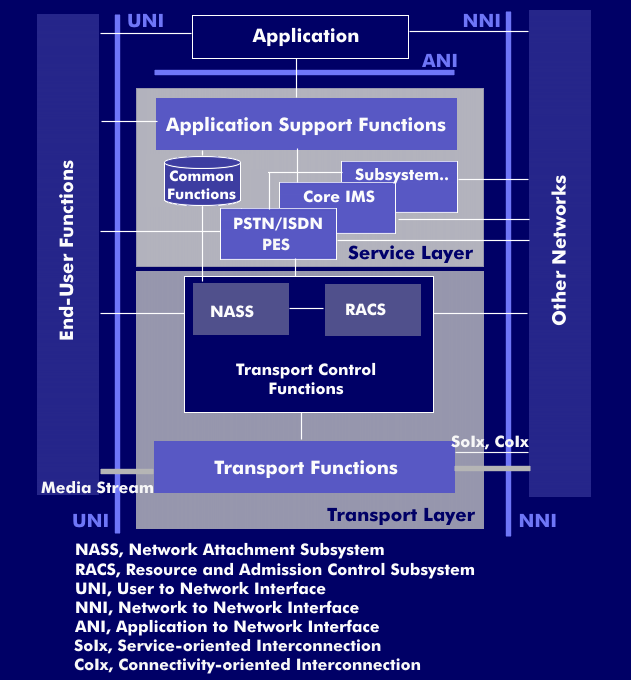
The NGN architecture, Next Generation Network (NGN), was defined by the International Telecommunication Union ( ITU) and the European Telecommunications Standards Institute( ETSI), taking into account the work of the Third Generation Partnership Project( 3GPP). The NGN architecture model is specified in ITU Recommendation Y.2012. According to this architecture, Next Generation Networks (NGN) supported multimedia services and content-basedservices, including streaming media and broadcast.
The NGN architecture defines the various interfaces, the Network to Network Interface( NNI) between the NGN and other networks, the User Network Interface( UNI) for user interfaces, and the Application Network Interface( ANI) for application interfaces. The NGN architecture model is divided into two layers: The transport plane and the application plane. The transport plane supports IP connections and is controlled by transport control functions. These control functions include the Network Attachment Control Functions( NACF) and the Resource and Admission Control Functions( RACF).
At the transport level, there are two subsystems, the Network Attachment Subsystem( NASS) and the Resource Admission Control Subsystem( RACS), which control access authorizations and IP address assignment. Above the transport layer is the application layer, which contains the core network area and service management.
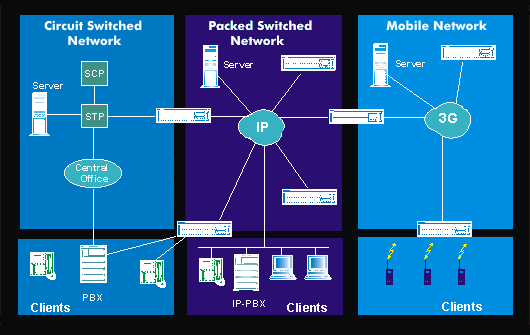
The access layer is where subscribers and terminals are connected to the Next Generation Network. At this level, the various information and transmission formats of circuit-switched networks, packet-switched IP networks, intelligent networks and mobile networks must be converted into information that can be understood by the Next Generation Network. Accordingly, the components for connecting business and residential customers are located in the access area; thus, with the Access Media Gateway( AMG), the standard interface for residential customers, with the Integrated Access Device( IAD), the interface for business customers, the components for signaling, the Signalling Gateway( SGW), for connecting packet and circuit-switched networks, the Trunk Media Gateway( TMG) and the Universal Media Gateway( UMG) for mobile networks.
In the Next Generation Network, the core network is an IP network. Such a network consists of a uniform transport platform, IP routers and Layer 3 switches. The network control layer is formed by softswitches, which take over the connection control of the individual components.
In the service management layer, services, value-added services and supplementary services are provided and transmitted via the existing connections.