MPEG-2
The MPEG standard MPEG-2, ISO/ IEC 13814, adopted in 1994, is suitable for the transmission of moving images in standard television quality and studio quality with multiple audio channels. These television standards are specified in the ITUBT.601file format. MPEG-2 builds on MPEG-1 and takes interlaced scanning into account. In terms of resolution, the video portion of MPEG-2 ranges from low television quality, Low Definition Television( LDTV), to standard television quality, Standard Definition Television( SDTV), to high definition television( HDTV).
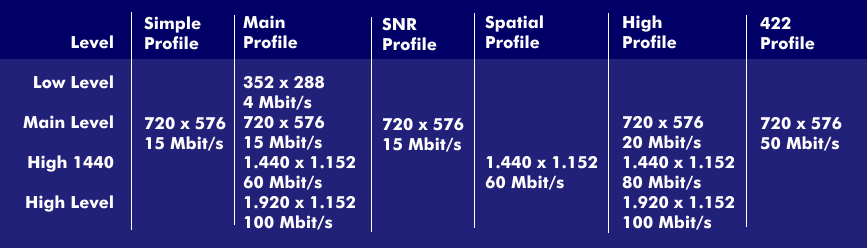
The profiles of MPEG-2
MPEG-2, standardized to H.262, has several profiles, some of which are scalable; this means that video sequences with different picture quality can be created from existing video data streams. The different profiles represent video displays with resolutions between 352 x 288 (Low), 720 x 576 (Main) and HDTV with 1,440 x 1,152 or 1,920 x 1,152 (High) pixels with an aspect ratio of 16:9. To be able to compress studio recordings in high quality, MPEG-2 has a color subsampling of 4:2:2 with the 422 profile.
The Main profile and the Main level are among the most widely used profiles, especially in DVDs and digital TV. The High profile, in combination with the High level, is aimed at HDTV. The resulting data rates range from 4 Mbits/s to 166 Mbits/s and are compressed by factors between 10:1 and 40:1, resulting in an MPEG-2 stream of 4 Mbits in the case of the 166 Mbits/s stream.
MPEG-2 and audio
MPEG-2 supports corresponding audio sequences, which are multiplexed before transmission and then transmitted as a transport stream and synchronized with the video sequences. MPEG-2 audio is compatible with MPEG-1 audio and also provides AAC compression.
Like MPEG-1 audio, MPEG-2 audio is optimized for lossy compression of high-quality audio signals. In addition to the sampling rates of 32 kHz, 44.1 kHz, and 48 kHz also used in MPEG-1 audio, MPEG-2 audio also allows sampling rates of 8 kHz, 11 kHz, 16 kHz, 22 kHz, 24 kHz, and 96 kHz, which are used in voice compression in ISDN, G.721, or online distribution, cinema, and audio studio applications.
MPEG-2 audio supports HDTV, Digital Theatre Sound( DTS) and Dolby Digital with up to 7 audio channels and low frequency channel (7.1) with depth enhancement( LFE). Channel encoding is very flexible, with up to 48 audio channels that can be combined to create surround sound. In addition to the capabilities of MPEG-1 audio - mono (1.0), stereo (2.0) and joint ster eo - MPEG-2 offers Intensity Stereo Coding ( ISC), Phantom Coding of Center Channel( PCC), Dynamic Transmission Channel Switching, Dynamic Cross Talk and Adaptive Multichannel Prediction.
MPEG-2 is also designed for client- server applications and can be distributed over heterogeneous networks. MPEG-2 is the basic technology for DVDs; however, it is also used in Digital Video Broadcasting( DVB) and in set-top boxes.
The extension of MPEG-2 specifications to HDTV allowed MPEG-3, originally designed for high-definition television (HDTV), to be abandoned in favor of MPEG-2.