IPv6 address
The IPv6 address differs essentially from the IPv4 address, which has an address range of 32 bits, by the enormous address space of 128 bits. Due to this extended address space, an almost infinite number of addressable nodes can be addressed; the number of addresses corresponds to that of a 39- digit decimal number.
Unlike the IPv4 address, the IPv6 addresses are not represented in four decimal numbers, but with eight alphanumeric combinations of the hexadecimal system. Instead of separating dots, the number groups of the IPv6 address are separated by colons and leading zeros are suppressed. Thus, an IPv6 address looks like this: 221:4033:a450:fb3:8a8b:56:ad:1234.
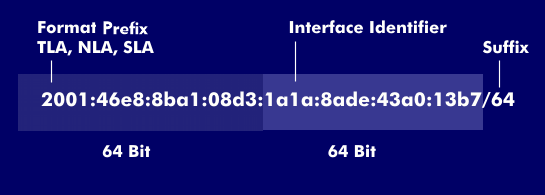
To avoid losing track in this addressing range, the 128 bits are divided into eight blocks of 16 bits each. The first four blocks, i.e. 64 bits, are used for routing and denote the network prefix, while the following 64 bits denote the interface identifiers (interface ID) for interface identification in subnets.
The format of the IPv6 address
The simplest form of an IPv6 address comprises 128 bits as the node address. By means of a format prefix( FP) certain address formats are preset. Thus the formats for unicast, multicast and for some protocol-dependent address extensions. The address structure is characterized by several levels that represent the addresses of areas, subnets and interfaces. These hierarchy levels or layers greatly simplify the routing and autoconfiguration of addresses. Stateless autoconfiguration of IPv6 addresses is supported by Stateless Address Autoconfiguration( SLAAC).
If the routers in the Internet backbone with IPv4 still need the complete IP addressing and all routes, the effort in IPv6 is reduced to the relevant address part entered in the respective level aggregation, the Top Level Aggregation( TLA), the Next Level Aggregation( NLA) and the Site Level Aggregation( SLA). These aggregation fields, together with the format prefix, occupy 64 bits of the IPv6 address. The remaining 64 bits are occupied by the Interface Identifier, a globally unique identification of nodes and interfaces formatted in the Extended Unique Identifier( EUI).
As with the IPv4 address, the notation of the IPv6 address is done in Classless Interdomain Routing( CIDR) with a suffix whose value is separated by a slash and which determines the number of subnet classes.


-Unicast-Adresse-(unten)_en.png)