IEEE 802.3ap
The 802.3ap working group, which began its work in 2004, is working on the specifications for using 10 Gigabit Ethernet as backplane Ethernet. This is Ethernet for short distances of less than one meter that can be used in backplanes of blade servers. Backplane Ethernet can replace proprietary backplane solutions and provides an approach that allows blades from different vendors to be combined in a rack.
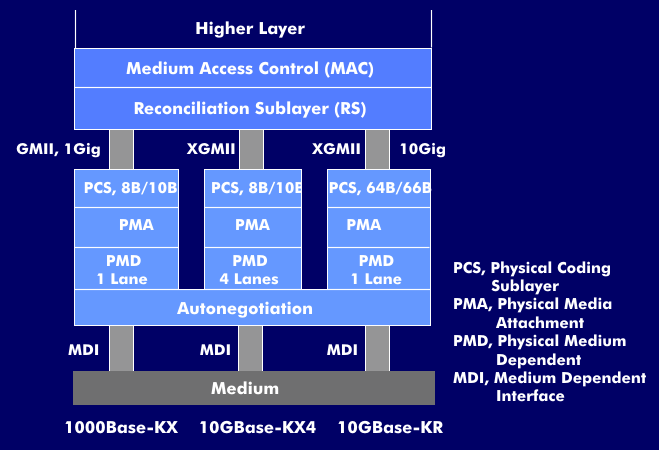
The specifications developed by the 802.3ap working group are compatible with Ethernet in the media access method( MAC) and frame format, so the adaptation is done at the physical layer. The minimum and maximum frame length of the 802.3 frame is maintained and the Medium Dependent Interface( MDI) is supported. Backplane Ethernet will be routed directly over the backplane at data rates of 1 Gbps and 10 Gbps and will support auto-negotiation for automatic speed matching to other interfaces.
The connection specified by 802.3ap is a point-to-point connection with two connectors. There are a total of three versions with the interfaces 1000Base-KX, 10GBase-KX4 and 10GBase-KR. 1000Base-KX is a serial port with a data rate of 1 Gbit/s and a signaling rate of 1.25 GBaud.
10GBase-KX4 is based on four lanes with a baud rate of 3.125 GBaud each and reaches a data rate of 10 Gbit/s, and 10GBase-KR is a serial port with 10 Gbit/s data rate. This connection works with one pair of wires and with 10.315 GBaud. Autonegotiation allows the interfaces to use the highest possible data rate.