IEEE 802.11ad
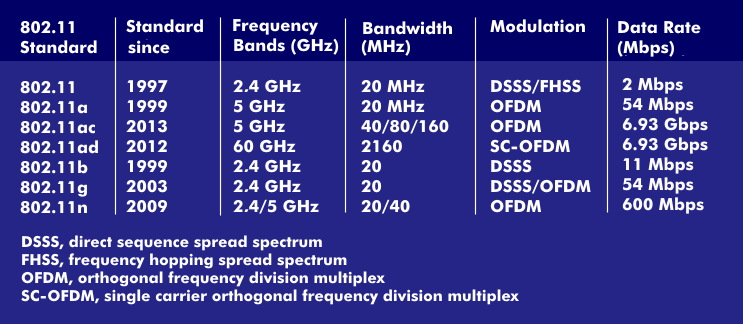
IEEE 802.11ad, developed by the Wireless Gigabit Alliance(WiGig) and standardized in 2012, is the only one of the 802.11 WLANs to operate in the license-free 60 GHz band. Due to its high free- space attenuation, 802.11ad is not designed for multi- user networks, but for point-to-point connections with single input single output( SISO) over short distances with line-of-sight( LOS) links. Data rates of up to 6.8 Gbit/s are possible with 802.11ad. It is thus in direct competition with Wireless HDMI(WHDMI), which achieves data rates of 4 Gbit/s.
Compared to the 5 GHz band used by 802.11a, 802 .11n and 802.11ac, the 60 GHz band has a transmission bandwidth that can transmit several gigabits per second. While 802.11ac must use sophisticated coding, modulation and multiplexing to make the best use of the available bandwidth, 802.11ad has a bandwidth of over eight gigahertz.
The 60 GHz band is divided into four channels for 802.11ad, each with a bandwidth of 2.16 GHz. The center frequencies of the four bandpasses recommended by the ITU-R are 58.32 GHz, 60.48 GHz, 62.64 GHz and 64.80 GHz. As modulation, 802.11ad uses SC- OFDM, a single- carrier variant of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplex (OFDM). To improve transmission conditions, 802.11ad relies on beamforming, in which the radiation characteristics of the antennas are aligned with each other, thereby increasing the field strength. With these techniques, 802.11ad achieves data transmission rates ofup to 6.76 Gbit/s.
The 802 .11ay standard, which was published later, is an extension of 802.11ad. This standard is characterized by a data rate of 20 Gbit/s and some technical changes.