ExpressCard
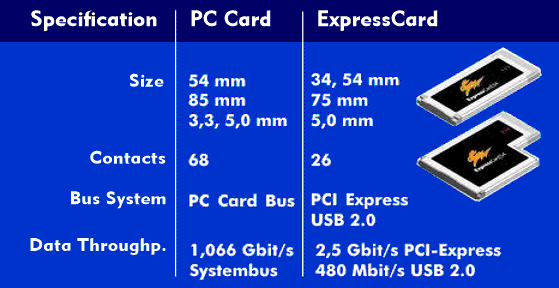
The ExpressCard is the successor card to the PC Card, which like the latter was specified by the PCMCIA Association and standardized by the International Telecommunication Union( ITU). There is one major difference between the two aforementioned memory cards apart from their size: the PC Card was operated via the PC Card bus and the PC Card controller, while the ExpressCard is connected via the PCI Express( PCIe) or the USB interface 2.0.
This has an effect on the data throughput, which can be a maximum of 2.5 Gbit/s for the PCI-Express x1 lane and 480 Mbit/s for USB 2.0. In contrast, the PC Card bus has to share the system bus data rate of 1.066 Gbit/s with other components.
ExpressCard operates with a supply voltage of 1.5 V and 3.3 V and therefore have a low power consumption.
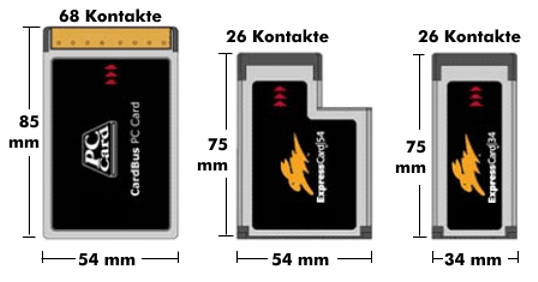
The ExpressCard is available in two versions with different widths: ExpressCard 34 and ExpressCard 54. Both have the same number of contacts and pinout. The smaller 34 card is designed to fit into the slot of the 54 card. However, neither card is backward compatible with the PC card.
The ExpressCard can be used for notebook extensions, WLANs and mobile communications, for network and sound cards, for memory cards and communication interfaces, for Firewire, Gigabit Ethernet, WiMAX and DVB, and for many more applications.