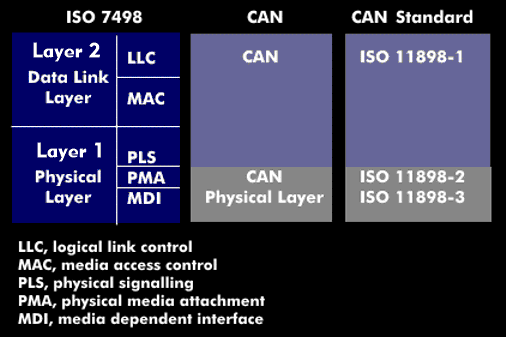
CAN protocol
The CAN bus operates in multimaster mode, in which the content of the CAN data frame transmitted via the field bus is identified by identifiers. Each station connected to the CAN bus can receive the message and utilize it. For this purpose, the stations read the identifier and use it to determine whether the message is relevant to them, e.g. speed, temperature, pressure.
This procedure allows each station to interact simultaneously on the same message. To avoid collisions on the bus, the CAN bus uses arbitration and prioritization. Priorities are assigned to the identifiers and the message with the highest priority is given priority. The CAN bus is allocated bit by bit. There are two bit formats of different lengths for the identifier that can coexist on the CAN bus: the standard identifier with 11 bits and the extended identifier with 29 bits.
Since some bits are transmitted in the CAN data frame for the cyclic block check, the data frame check and for further error detection procedures, it can only hold a few bytes ofuser data. This has the advantage that the time loss for the repetition of the data frame is very small in case of an error detection.