Bluetooth standard
Bluetooth is a standard for in-house communication via radio. The Bluetooth standard was developed in 1998 by Ericsson, IBM, Intel, Nokia and Toshiba and aims to support short-range communication between end devices such as notebooks, smartphones, tablets, PDAs and cell phones.
The Bluetooth standard specifies a transmit power of 1 mW (0 dBm), which limits the distance for communication to a few meters. The sensitivity of the radio receivers is -70 dBm. In addition to this transmission power, which is referred to as transmission class 3, there is alternatively transmission class 1 with 100 mW (20 dBm) with a distance of up to 100 m and transmission class 2 with 2.5 mW (4 dBm) with a range of 10 m.
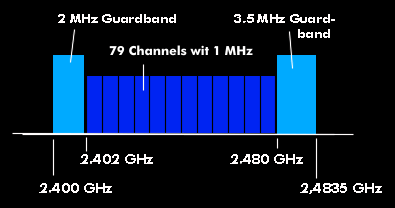
Bluetooth operates in the microwave range between 2 . 402 GHz and 2.480 GHz, the ISM band with frequency hopping( FHSS). The frequency band is terminated at 2.402 MHz by a 2 MHz wide guard frequency band, and at 2.48 GHz the guard band is 3.5 MHz wide. The channel width of the 79 channels is 1 MHz, and the frequency jumps between 79 frequencies up to 1,600 times per second (FHSS). The Bluetooth air interface uses GFSK modulation.
Bluetooth provides a wideband connection channel for the transmission of voice and data. Up to three voice channels can be operated simultaneously at 64 kbit/s, with conversion using Continuous Variable Slope Delta Modulation( CVSD) or the A-Law method. The channel distribution for the upstream and downstream can be symmetrical with a maximum data rate of 432.6 kbit/s or asymmetrical with a transmission rate of 723.2 kbit/s for the downstream and 57.6 kbit/s for the upstream channel. This data rate corresponds to the Basic Rate( BR) operating mode. With Enhanced Data Rate( EDR) and Differential Quaternary PhaseShift Keying( DQPSK), the data rate is three times higher at 2.167 Mbit/s.
In order to receive messages, the receivers must be synchronized to the transmitter's hop sequence. Synchronization signals are sent by the master for this purpose. The individual Bluetooth components are identified by a unique 48-bitBluetooth address. This regulates the rights, functions and security of the participants communicating with each other.
The different Bluetooth versions
In Bluetooth 1.0, data was exchanged without any special security protection; this was provided exclusively by the FHSS method, whose algorithm ensures a high level of eavesdropping security. Since radio networks have a lower level of protection than wired networks, Bluetooth security is of particular importance. Bluetooth distinguishes between three security levels: the first level knows no security mechanisms, the second knows flexible accesses for different security requirements, and in the third level, the security procedures are already initialized when the connection is established. Bluetooth 1.1 supports Adaptive Frequency Hopping( AFH) and has an indicator for the received signal strength, the Received Signal Strength Indicator( RSSI). Bluetooth 2.0 supports Quality of Services( QoS).
As part of Bluetooth development, Bluetooth 3.0 implemented Bluetooth High Speed( BHS) with data rates of 3 Mbps, and Bluetooth 4.0 was designed as an energy-efficient Bluetooth standard: Bluetooth Low Energy( BLE).
The BLE specification is suitable for the Internet of Things( IoT), building automation and the transmission of sensor values, for example in telemedicine, sports and fitness applications. Bluetooth 4.0 distinguishes between two different types of devices: smart devices and smart ready devices. Smart Devices are small sensors such as those used in a Body Area Network( BAN) to record certain bodily functions and transmitted via Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), whereas Smart Ready Devices are built into smartphones, tablets or consumer electronics devices. Smart Ready Devices typically have a dual-mode RF part and can also operate at Enhanced Data Rate (EDR).
Bluetooth 5, designed for the Internet of Things (IoT), extends the characteristic values of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). For example, the data rate of Bluetooth 5 has been increased to 2 Mbit/s, the expansion range has been extended to 40 m and the transmission capacity has been increased eightfold. Bluetooth 5 also supports up to five beacons and thus increases the location accuracy of people and products.